Context
This project is the end of term assignment in the Discriminant Analysis course led by Prof. Salim Lardjane, UBS.
Goals
The project has 2 main goals:
- be familiar with standard machine learning models
- implement from scratch those algorithms to understand the underlying statistics
Loading in the libraries
We’ll be reading a file containing information regarding the financial situation of a person to know weather this person is fit to pay the default or not.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
library(foreign)
library(MASS)
library(ROCR)
library(mlogit)
library(caTools)
library(e1071)
library(ggplot2)
library(ROCit)
library("tidyverse")
data <- read.spss("./bankloan.sav",to.data.frame=TRUE)
Descriptive analysis
1
summary(data)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
## age ed employ
## Min. :20.00 Did not complete high school:460 Min. : 0.000
## 1st Qu.:29.00 High school degree :235 1st Qu.: 3.000
## Median :34.00 Some college :101 Median : 7.000
## Mean :35.03 College degree : 49 Mean : 8.566
## 3rd Qu.:41.00 Post-undergraduate degree : 5 3rd Qu.:13.000
## Max. :56.00 Max. :33.000
## address income debtinc creddebt
## Min. : 0.000 Min. : 13.00 Min. : 0.10 Min. : 0.0117
## 1st Qu.: 3.000 1st Qu.: 24.00 1st Qu.: 5.10 1st Qu.: 0.3822
## Median : 7.000 Median : 35.00 Median : 8.70 Median : 0.8851
## Mean : 8.372 Mean : 46.68 Mean :10.17 Mean : 1.5768
## 3rd Qu.:12.000 3rd Qu.: 55.75 3rd Qu.:13.80 3rd Qu.: 1.8984
## Max. :34.000 Max. :446.00 Max. :41.30 Max. :20.5613
## othdebt default preddef1 preddef2
## Min. : 0.04558 No :517 Min. :0.0001166 Min. :0.0000387
## 1st Qu.: 1.04594 Yes :183 1st Qu.:0.0456301 1st Qu.:0.0351757
## Median : 2.00324 NA's:150 Median :0.1715129 Median :0.1590730
## Mean : 3.07879 Mean :0.2585762 Mean :0.2578660
## 3rd Qu.: 3.90300 3rd Qu.:0.4073259 3rd Qu.:0.4332770
## Max. :35.19750 Max. :0.9993967 Max. :0.9994570
## preddef3
## Min. :0.07464
## 1st Qu.:0.13476
## Median :0.20010
## Mean :0.25858
## 3rd Qu.:0.32863
## Max. :0.94810
Discriminant Analysis without cross-validation
Separating the data (train/test)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
library(MASS)
library(e1071)
na <- c(701:850)
apred <- data[na,] # the data that we're going to predict later on, once our models are trained
data2 <- subset(data, data$default != "NA'S") # the data we'll use for the train/test datasets
data2<-data2[1:9]
data2<-data2[-2]
data2[,8]<-as.numeric(data2$default)-1
n = dim(data2)[1]
id = sample(1:n,floor(0.75*n),replace=F)
train <- data2[id,]
test <- data2[-id,]
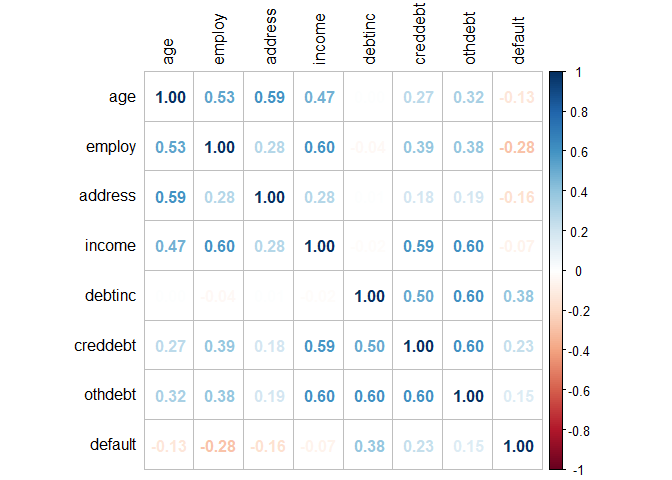
Correlation coefficient visualization
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
library(corrplot)
corrplot(cor(train), # Correlation matrix
method = "number", # Correlation plot method
type = "full", # Correlation plot style (also "upper" and "lower")
diag = TRUE, # If TRUE (default), adds the diagonal
tl.col = "black", # Labels color
bg = "white", # Background color
title = "", # Main title
col = NULL) # Color palette
Graphs
In order to find the best way to represent our data, we’ll sort the variables in 3 classes : stability, demographic and financial data.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
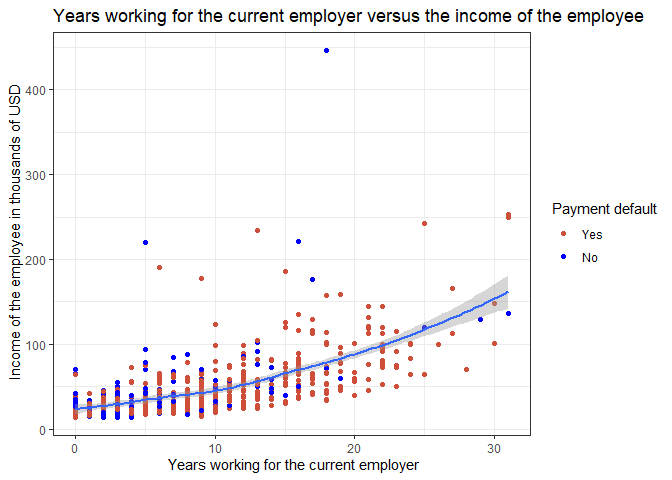
# stability variables : employ address
# demographic variables : age
# financial variables : income debtinc creddebt othdebt
# employ income
data2 %>% mutate(default = factor(default)) %>%
ggplot(aes(x = employ, y = income)) +
geom_point(mapping = aes(color = default)) +
labs(x=" Years working for the current employer",
y=" Income of the employee in thousands of USD",
color = "Payment default") +
geom_smooth() +
scale_color_manual(values = c("0" = "tomato3",
"1" = "blue"),
labels = c("Yes",
"No")) +
theme_bw()+
ggtitle("Years working for the current employer versus the income of the employee")
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
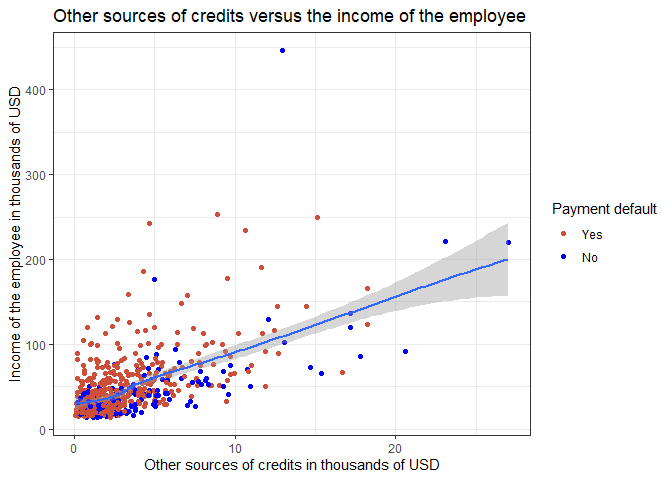
# othdebt income
data2 %>% mutate(default = factor(default)) %>%
ggplot(aes(x = othdebt, y = income)) +
geom_point(mapping = aes(color = default)) +
labs(y="Income of the employee in thousands of USD",
x="Other sources of credits in thousands of USD",
color = "Payment default") +
geom_smooth() +
scale_color_manual(values = c("0" = "tomato3",
"1" = "blue"),
labels = c("Yes",
"No")) +
theme_bw()+
ggtitle("Other sources of credits versus the income of the employee")
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
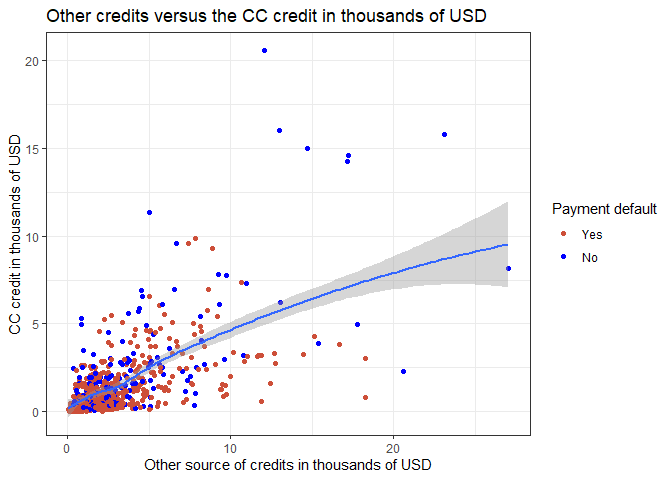
# othdebt creddebt
data2 %>% mutate(default = factor(default)) %>%
ggplot(aes(x = othdebt, y = creddebt)) +
geom_point(mapping = aes(color = default)) +
labs(y="CC credit in thousands of USD",
x="Other source of credits in thousands of USD",
color = "Payment default") +
geom_smooth() +
scale_color_manual(values = c("0" = "tomato3",
"1" = "blue"),
labels = c("Yes",
"No")) +
theme_bw()+
ggtitle("Other credits versus the CC credit in thousands of USD")
Defining the ROC function
This function will allow us to trace a ROC curve for each model that returns posterior probabilities
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
roc <- function(post1, col){
trapeze <- function(ao,bo) {
k <- length(ao)
iz <- 0
for (i in 1:(k-1)) {
iz <- iz+(ao[i+1]-ao[i])*(bo[i]+bo[i+1])/2
}
return(iz)
}
delta=0.001
valeurs <- seq(0,1,delta)
N <- length(valeurs)
sensibilite <- rep(NA,N)
antispec <- rep(NA,N)
i <- 0
for (u in valeurs) {
i <- i+1
pr2predict <- (post1>u)+0
TN1 <- sum((pr2predict==0)*(test$default==0))
FP1 <- sum((pr2predict==1)*(test$default==0))
FN1 <- sum((pr2predict==0)*(test$default==1))
TP1 <- sum((pr2predict==1)*(test$default==1))
Rap1 <- TP1/(TP1+FN1)
Pre1 <- TP1/(TP1+FP1)
F_sco1 <- (2*TP1)/(2*TP1+FP1+FN1)
Spe1 <- TN1/(FP1+TN1)
Err1 <- ((FP1+FN1)/(TN1+FP1+TP1+FN1)*100)
sensibilite[i] <- Rap1
antispec[i] <- 1-Spe1
}
antispec<- c(0,rev(antispec),1)
sensibilite <- c(0,rev(sensibilite),1)
plot(antispec,sensibilite,type="s",col=col,lwd=1)
return(trapeze(antispec, sensibilite))
}
Defining the models
For each model we’ll compute recall, f-score, acc, specificity and add the values to a dataframe that we’ll comment at the end.
Closest Mean method
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
no.age <- mean(train[train$default==0,]$age)
yes.age <- mean(train[train$default==1,]$age)
no.employ <- mean(train[train$default==0,]$employ)
yes.employ <- mean(train[train$default==1,]$employ)
no.address <- mean(train[train$default==0,]$address)
yes.address <- mean(train[train$default==1,]$address)
no.income <- mean(train[train$default==0,]$income)
yes.income <- mean(train[train$default==1,]$income)
no.debtinc <- mean(train[train$default==0,]$debtinc)
yes.debtinc <- mean(train[train$default==1,]$debtinc)
no.creddebt <- mean(train[train$default==0,]$creddebt)
yes.creddebt <- mean(train[train$default==1,]$creddebt)
no.othdebt <- mean(train[train$default==0,]$othdebt)
yes.othdebt <- mean(train[train$default==1,]$othdebt)
prediction <- function(x,y,z,a,b,c,d) {
if ((x-yes.age)^2+(y-yes.employ)^2+(z-yes.address)^2+(a-yes.income)^2+(b-yes.debtinc)^2+(c-yes.creddebt)^2+(d-yes.othdebt)^2 >(x-no.age)^2+(y-no.employ)^2+(z-no.address)^2+(a-no.income)^2+(b-no.debtinc)^2+(c-no.creddebt)^2+(d-no.othdebt)^2)
{
return(1)
} else {return(0)}
}
pred <- rep(NA,length(test$default))
for (i in 1:length(test$default)) {
pred[i] <- prediction(test$age[i],test$employ[i],test$address[i], test$income[i], test$debtinc[i], test$creddebt[i], test$othdebt[i])
}
MCPPM = table(pred,test$default)
MCPPMerr = (MCPPM[2,1]+MCPPM[1,2])/sum(MCPPM)
MCPPMrappel = MCPPM[2,2]/(MCPPM[2,2]+MCPPM[1,2])
MCPPMprecision = MCPPM[2,2]/(MCPPM[2,2]+MCPPM[2,1])
MCPPMF = 2*MCPPM[2,2]/(2*MCPPM[2,2]+MCPPM[2,1]+2*MCPPM[1,2])
MCPPMspecificite = MCPPM[2,2]/(MCPPM[2,2]+MCPPM[2,1])
PPM = round(c(MCPPMerr,MCPPMrappel,MCPPMprecision,MCPPMF,MCPPMspecificite),2)
Quadratic Discriminant Analysis method
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
library(MASS)
model = predict(qda(default~.,train),test)
MCqda = table(test$default,model$class) # correlation matrix
MCqdaerr = (MCqda[2,1]+MCqda[1,2])/sum(MCqda)
MCqdarappel = MCqda[2,2]/(MCqda[2,2]+MCqda[1,2])
MCqdaprecision = MCqda[2,2]/(MCqda[2,2]+MCqda[2,1])
MCqdaF = 2*MCqda[2,2]/(2*MCqda[2,2]+MCqda[2,1]+2*MCqda[1,2])
MCqdaspecificite = MCqda[2,2]/(MCqda[2,2]+MCqda[2,1])
qda = round(c(MCqdaerr,MCqdarappel,MCqdaprecision,MCqdaF,MCqdaspecificite),2)
Linear Discriminant Analysis method
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
library(MASS)
model = predict(lda(default~.,train),test)
MClda = table(test$default,model$class)
MCldaerr = (MClda[2,1]+MClda[1,2])/sum(MClda)
MCldarappel = MClda[2,2]/(MClda[2,2]+MClda[1,2])
MCldaprecision = MClda[2,2]/(MClda[2,2]+MClda[2,1])
MCldaF = 2*MClda[2,2]/(2*MClda[2,2]+MClda[2,1]+2*MClda[1,2])
MCldaspecificite = MClda[2,2]/(MClda[2,2]+MClda[2,1])
lda = round(c(MCldaerr,MCldarappel,MCldaprecision,MCldaF,MCldaspecificite),2)
Naive Bayes method
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
library(e1071)
model = predict(naiveBayes(default~.,train),test)
MCbayes = table(test$default,model)
MCbayeserr = (MCbayes[2,1]+MCbayes[1,2])/sum(MCbayes)
MCbayesrappel = MCbayes[2,2]/(MCbayes[2,2]+MCbayes[1,2])
MCbayesprecision = MCbayes[2,2]/(MCbayes[2,2]+MCbayes[2,1])
MCbayesF = 2*MCbayes[2,2]/(2*MCbayes[2,2]+MCbayes[2,1]+2*MCbayes[1,2])
MCbayesspecificite = MCbayes[2,2]/(MCbayes[2,2]+MCbayes[2,1])
bayes = round(c(MCbayeserr,MCbayesrappel,MCbayesprecision,MCbayesF,MCbayesspecificite),2)
K closest neighbours method
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
library(class)
cl <- as.factor(train$default)
predtest <- knn(train,test,cl, k=1)
MCknn1 = table(test$default,predtest)
MCknn1err = (MCknn1[2,1]+MCknn1[1,2])/sum(MCknn1)
MCknn1rappel = MCknn1[2,2]/(MCknn1[2,2]+MCknn1[1,2])
MCknn1precision = MCknn1[2,2]/(MCknn1[2,2]+MCknn1[2,1])
MCknn1F = 2*MCknn1[2,2]/(2*MCknn1[2,2]+MCknn1[2,1]+2*MCknn1[1,2])
MCknn1specificite = MCknn1[2,2]/(MCknn1[2,2]+MCknn1[2,1])
knn1 = round(c(MCknn1err,MCknn1rappel,MCknn1precision,MCknn1F,MCknn1specificite),2)
predtest <- knn(train,test,cl, k=2)
MCknn2 = table(test$default,predtest)
MCknn2err = (MCknn2[2,1]+MCknn2[1,2])/sum(MCknn2)
MCknn2rappel = MCknn2[2,2]/(MCknn2[2,2]+MCknn2[1,2])
MCknn2precision = MCknn2[2,2]/(MCknn2[2,2]+MCknn2[2,1])
MCknn2F = 2*MCknn2[2,2]/(2*MCknn2[2,2]+MCknn2[2,1]+2*MCknn2[1,2])
MCknn2specificite = MCknn2[2,2]/(MCknn2[2,2]+MCknn2[2,1])
knn2 = round(c(MCknn2err,MCknn2rappel,MCknn2precision,MCknn2F,MCknn2specificite),2)
predtest <- knn(train,test,cl,k=3)
MCknn3 = table(test$default,predtest)
MCknn3err = (MCknn3[2,1]+MCknn3[1,2])/sum(MCknn3)
MCknn3rappel = MCknn3[2,2]/(MCknn3[2,2]+MCknn3[1,2])
MCknn3precision = MCknn3[2,2]/(MCknn3[2,2]+MCknn3[2,1])
MCknn3F = 2*MCknn3[2,2]/(2*MCknn3[2,2]+MCknn3[2,1]+2*MCknn3[1,2])
MCknn3specificite = MCknn3[2,2]/(MCknn3[2,2]+MCknn3[2,1])
knn3 = round(c(MCknn3err,MCknn3rappel,MCknn3precision,MCknn3F,MCknn3specificite),2)
Logistic regression model
Preparing the data
1
data2$default <- as.factor(data2$default)
Defining the model
1
2
3
4
5
6
reglog <- glm(default~., family = binomial, data=train, control=list(maxit=1000, trace=TRUE, epsilon=1e-16))
preds <- predict(reglog, test, type='response')
optimal_cutoff <- ifelse(preds > 0.5, 1, 0)
summary(reglog)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
##
## Call:
## glm(formula = default ~ ., family = binomial, data = train, control = list(maxit = 1000,
## trace = TRUE, epsilon = 1e-16))
##
## Deviance Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -2.3241 -0.6734 -0.3020 0.2628 2.6057
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept) -1.657904 0.664307 -2.496 0.0126 *
## age 0.044607 0.020375 2.189 0.0286 *
## employ -0.268156 0.037089 -7.230 4.82e-13 ***
## address -0.113424 0.027131 -4.181 2.91e-05 ***
## income -0.008652 0.008473 -1.021 0.3072
## debtinc 0.067861 0.035900 1.890 0.0587 .
## creddebt 0.611694 0.134228 4.557 5.19e-06 ***
## othdebt 0.080870 0.085357 0.947 0.3434
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## (Dispersion parameter for binomial family taken to be 1)
##
## Null deviance: 602.75 on 524 degrees of freedom
## Residual deviance: 418.16 on 517 degrees of freedom
## AIC: 434.16
##
## Number of Fisher Scoring iterations: 7
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
#confusion matrix
MCreg = table(test$default, optimal_cutoff)
MCregerr = (MCreg[2,1]+MCreg[1,2])/sum(MCreg)
MCregrappel = MCreg[2,2]/(MCreg[2,2]+MCreg[1,2])
MCregprecision = MCreg[2,2]/(MCreg[2,2]+MCreg[2,1])
MCregF = 2*MCreg[2,2]/(2*MCreg[2,2]+MCreg[2,1]+2*MCreg[1,2])
MCregspecificite = MCreg[2,2]/(MCreg[2,2]+MCreg[2,1])
reg = round(c(MCregerr,MCregrappel,MCregprecision,MCregF,MCregspecificite),2)
1
2
titles = c("Error rate","Recall","Accuracy","F-Score","Specificity")
data.frame(titles,lda,qda,knn1,knn2,knn3,PPM, reg)
1
2
3
4
5
6
## titles lda qda knn1 knn2 knn3 PPM reg
## 1 Error rate 0.19 0.21 0.29 0.30 0.24 0.54 0.18
## 2 Recall 0.70 0.66 0.46 0.42 0.56 0.22 0.68
## 3 Accuracy 0.50 0.46 0.46 0.35 0.39 0.14 0.59
## 4 F-Score 0.52 0.47 0.36 0.30 0.39 0.13 0.55
## 5 Specificity 0.50 0.46 0.46 0.35 0.39 0.14 0.59
Disciminant Analysis with cross-validation method Leave-One-Out
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
data2$default <- as.numeric(data2$default)-1
n = dim(data2)[1]
lda = 0
qda = 0
naive = 0
knn1 = 0
knn2 = 0
knn3 = 0
ppm = 0
for(i in 1:n) {
train <- data2[-i,]
test <- data2[i,]
# LDA #
model = predict(lda(default~.,train),test)
erlda = (data2$default[i] != model$class) + 0
MClda = table(model$class,test$default)
lda[i] = erlda
# QDA #
model2 = predict(qda(default~.,train),test)
erqda = (data2$default[i] != model2$class) + 0
qda[i] = erqda
# Naive Bayes #
model3 = predict(naiveBayes(default~.,train),test)
ernaive = (data2$default[i] != model3) + 0
naive[i] = ernaive
# KNN #
cl <- as.factor(train$default)
# Prediction K=1 #
predtest <- knn(train,test,cl, k=1)
# errors K=1 #
erknn1 = (data2$default[i] != predtest) + 0
knn1[i] = erknn1
# Prediction K=2 #
predtest <- knn(train,test,cl, k=2)
# errors K=2 #
erknn2 = (data2$default[i] != predtest) + 0
knn2[i] = erknn2
# Prediction K=3 #
predtest <- knn(train,test,cl, k=3)
# errors K=3 #
erknn3 = (data2$default[i] != predtest) + 0
knn3[i] = erknn3
# Prediction for closest mean #
no.age <- mean(train[train$default==0,]$age)
yes.age <- mean(train[train$default==1,]$age)
no.employ <- mean(train[train$default==0,]$employ)
yes.employ <- mean(train[train$default==1,]$employ)
no.address <- mean(train[train$default==0,]$address)
yes.address <- mean(train[train$default==1,]$address)
no.income <- mean(train[train$default==0,]$income)
yes.income <- mean(train[train$default==1,]$income)
no.debtinc <- mean(train[train$default==0,]$debtinc)
yes.debtinc <- mean(train[train$default==1,]$debtinc)
no.creddebt <- mean(train[train$default==0,]$creddebt)
yes.creddebt <- mean(train[train$default==1,]$creddebt)
no.othdebt <- mean(train[train$default==0,]$othdebt)
yes.othdebt <- mean(train[train$default==1,]$othdebt)
prediction <- function(x,z,a,b,c,d,e) {
if ((x-yes.age)^2+(z-yes.employ)^2+(a-yes.address)^2+
(b-yes.income)^2+(c-yes.debtinc)^2+(d-yes.creddebt)^2+
(e-yes.othdebt)^2 >
(x-no.age)^2+(z-no.employ)^2+(a-no.address)^2+
(b-no.income)^2+(c-no.debtinc)^2+(d-no.creddebt)^2+
(e-no.othdebt)^2)
{
return(1)
} else {return(0)}
}
pred <- prediction(test$age,test$employ,test$address, test$income, test$debtinc, test$creddebt, test$othdebt)
erppm = (data2$default[i] != pred) + 0
ppm[i] <- erppm
}
validationCroisée = c("taux d'erreur")
res = c(mean(lda),mean(qda),mean(naive),mean(knn1),mean(knn2),mean(knn3), mean(ppm))
lda = mean(lda)
qda = mean(qda)
naive = mean(naive)
knn1 = mean(knn1)
knn2 = mean(knn2)
knn3 = mean(knn3)
ppm = mean(ppm)
data.frame(validationCroisée,lda,qda,naive,knn1,knn2,knn3,ppm)
1
2
3
4
## validationCroisée lda qda naive knn1 knn2 knn3
## 1 taux d'erreur 0.1871429 0.2228571 0.2471429 0.2842857 0.2928571 0.2471429
## ppm
## 1 0.5414286
Here we can see that the model with the smallest error rate is the LDA model.
Using our best model for the prediction on the data
1
2
model = predict(lda(default~.,data2),apred)
model$class
1
2
3
4
5
6
## [1] 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
## [38] 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1
## [75] 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1
## [112] 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
## [149] 0 0
## Levels: 0 1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
yes = 0
no = 0
for (i in 1:150){
if(model$class[i] == 1){
yes=yes+1
}else{
no=no+1
}
}
yes
1
## [1] 23
1
no
1
## [1] 127
1
prediction = yes/150;prediction
1
## [1] 0.1533333
So out of 150 people, 23 are likely to repay their credit and 127 are not likely to repay their credit, iow -> 15.3% of the population
